Integrating Argos with Storybook and GitHub Actions: A Complete Guide
Set up Argos with Storybook and GitHub Actions to automate visual regression checks and keep UI quality high.

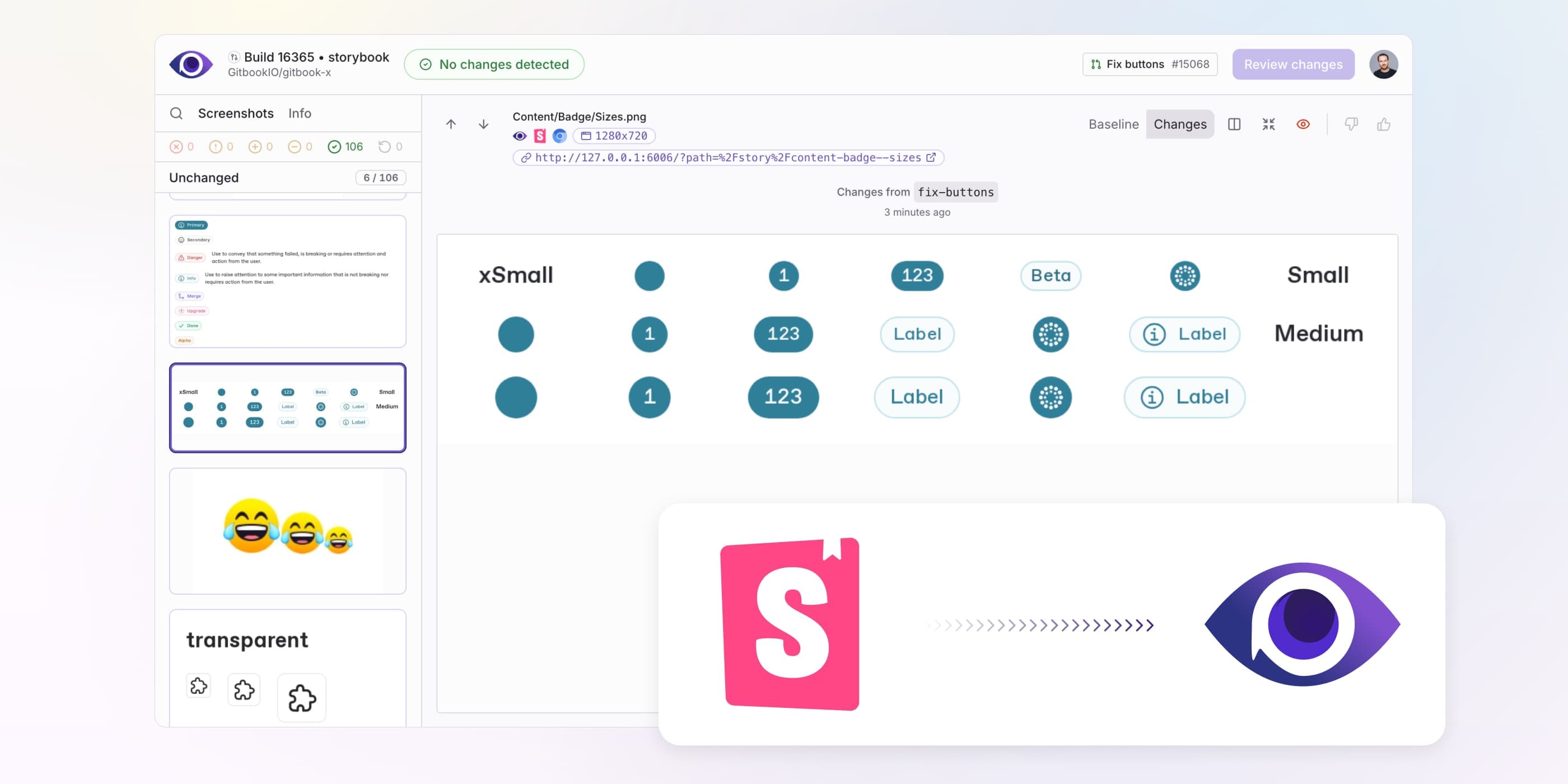
Visual regression testing is crucial for maintaining UI consistency. Argos automates this by comparing screenshots over time, catching visual changes early. By integrating Argos with Storybook and GitHub Actions, you can run visual regression tests directly within your CI/CD pipeline, catching issues early in development.
This guide provides a step-by-step walkthrough to integrate Argos with Storybook and GitHub Actions, ensuring any visual inconsistencies are caught during development.
Overview
- Prerequisites
- Setting Up Argos
- Configuring Storybook for Visual Testing
- Automating with GitHub Actions
- Conclusion
Prerequisites
Before beginning, make sure you have:
- A GitHub repository with Storybook already installed and configured.
- Basic knowledge of GitHub Actions and experience with CI/CD workflows.
Setting Up Argos
Follow these steps to configure Argos for your project:
1. Create an Argos Account
- Sign up at argos-ci.com using your GitHub account.
- Authorize Argos to access your repositories.
2. Add Your Repository
- In the Argos dashboard, click on Add a repository.
- Select the GitHub repository you want to integrate.
- Follow the setup instructions on the screen to complete the configuration.
3. Copy the Argos Token
- Go to the settings page for your repository on Argos.
- Copy the ARGOS_TOKEN; you’ll need it for your GitHub Actions configuration.
Configuring Storybook for Visual Testing
To capture screenshots, we’ll use the Storybook Test Runner and Argos SDK.
1. Install Dependencies
Add the necessary dependencies for the Storybook test runner and Argos SDK:
npm install --save-dev @argos-ci/cli @argos-ci/storybook @storybook/test-runner2. Update package.json Scripts
In your package.json, add scripts to build Storybook, run tests, and upload screenshots:
{
"scripts": {
"build-storybook": "build-storybook",
"test-storybook": "NODE_NO_WARNINGS=1 NODE_OPTIONS=--experimental-vm-modules test-storybook",
"upload-screenshots": "npm exec argos -- upload screenshots --build-name storybook"
}
}- The
test-storybookscript uses Storybook’s test runner to execute tests and capture screenshots. - The
upload-screenshotsscript uploads the screenshots to Argos for visual comparison.
Note: NODE_OPTIONS=--experimental-vm-modules is required due to Storybook’s reliance on Jest, which needs this flag to run modern packages like Argos Storybook SDK.
3. Add a .storybook/test-runner.ts File
Create a test-runner.ts file in your .storybook directory to configure screenshot capture:
// .storybook/test-runner.ts
import { argosScreenshot } from "@argos-ci/storybook";
import type { TestRunnerConfig } from "@storybook/test-runner";
const config: TestRunnerConfig = {
async postVisit(page, context) {
await argosScreenshot(page, context);
},
};
export default config;This configuration will capture screenshots of your stories in the ./screenshots directory. Be sure to add this directory to .gitignore.
4. Run Storybook Test Runner Locally
Run the Storybook test runner locally to verify screenshots are generated correctly:
npx test-storybookThis command will capture screenshots of your stories and save them to ./screenshots.
Automating with GitHub Actions
Next, we’ll set up GitHub Actions to automate visual regression testing. This example runs against a locally served Storybook instance.
1. Add ARGOS_TOKEN to GitHub Secrets
- In your GitHub repository, go to Settings > Secrets and variables > Actions.
- Click on New repository secret.
- Add a secret named
ARGOS_TOKENand paste in the token from Argos.
2. Create the GitHub Actions Workflow
Add the following workflow file to .github/workflows/storybook-tests.yml:
# .github/workflows/storybook-tests.yml
name: "Storybook Tests"
on:
pull_request:
push:
branches:
- main
jobs:
test:
timeout-minutes: 60
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version-file: ".nvmrc"
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install --frozen-lockfile
- name: Install Playwright
run: npx playwright install --with-deps
- name: Build Storybook
run: npm run build-storybook -- --quiet
- name: Serve Storybook and Run Tests
run: |
npx concurrently -k -s first -n "SB,TEST" -c "magenta,blue" \
"npx http-server storybook-static --port 6006 --silent" \
"npx wait-on tcp:127.0.0.1:6006 && npm run test-storybook && npm run upload-screenshots"
env:
ARGOS_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.ARGOS_TOKEN }}Note: Storybook outputs the build to storybook-static by default. If using a different output directory, adjust accordingly.
This workflow triggers on every push to main and on pull requests. It will build Storybook, serve it locally, run the tests, and upload screenshots to Argos.
Conclusion
By integrating Argos with Storybook and GitHub Actions, you now have a reliable automated visual regression testing setup. This process helps you catch visual inconsistencies early, ensuring UI stability and quality.
For advanced configurations, check the Argos documentation.